
STL_Functions_to_Know.pdf
0.27MB
<Functions to know how to use WITHOUT a description.>
Exam 2 - STL Functions to Know
Functions to know how to use WITHOUT a description.
- STL vector/list/set/multiset/map/multimap
- Constructors (all those included in the lessons)
- begin/end/rbegin/rend
- clear
- empty
- operator=
- size
- erase(first, last)
- STL vector
- at
- assign(first, last), assign(n, val)
- erase(position), erase(first, last)
- front, back
- insert(position, val), insert(position, n, val)
- operator[]
- pop_back, push_back
- reserve, resize
- swap
- STL list
- assign(first, last), assign(n, val)
- front, back
- pop_back, pop_front, push_back. push_front
- erase(position)
- insert(position, val), insert(position, n, val)
- merge (list x)
- remove(val), remove_if(predicate), sort()
- splice(position, x), splice(position, x, i), splice, position, x, first, last)
- swap(list x)
- unique()
- STL set/multiset/map/multimap
- count
- erase(val)
- insert(val), insert(first, last), insert(initializer list)
- swap
- STL map/multimap
- maps only: operator[]
- insert(make_pair)
- find
- STL stack
- Constructor
- empty
- pop
- push
- size
- swap (member function)
- top
- STL queue
- Constructor
- back
- empty
- front
- pop
- push
- size
- swap (member function)
- STL algorithms
- advance(position, n)
- next (position, n)
Functions to know how to use WITH a given description.
On the exam, you will have descriptions for the functions listed below.
Here is an example of an STL function description:
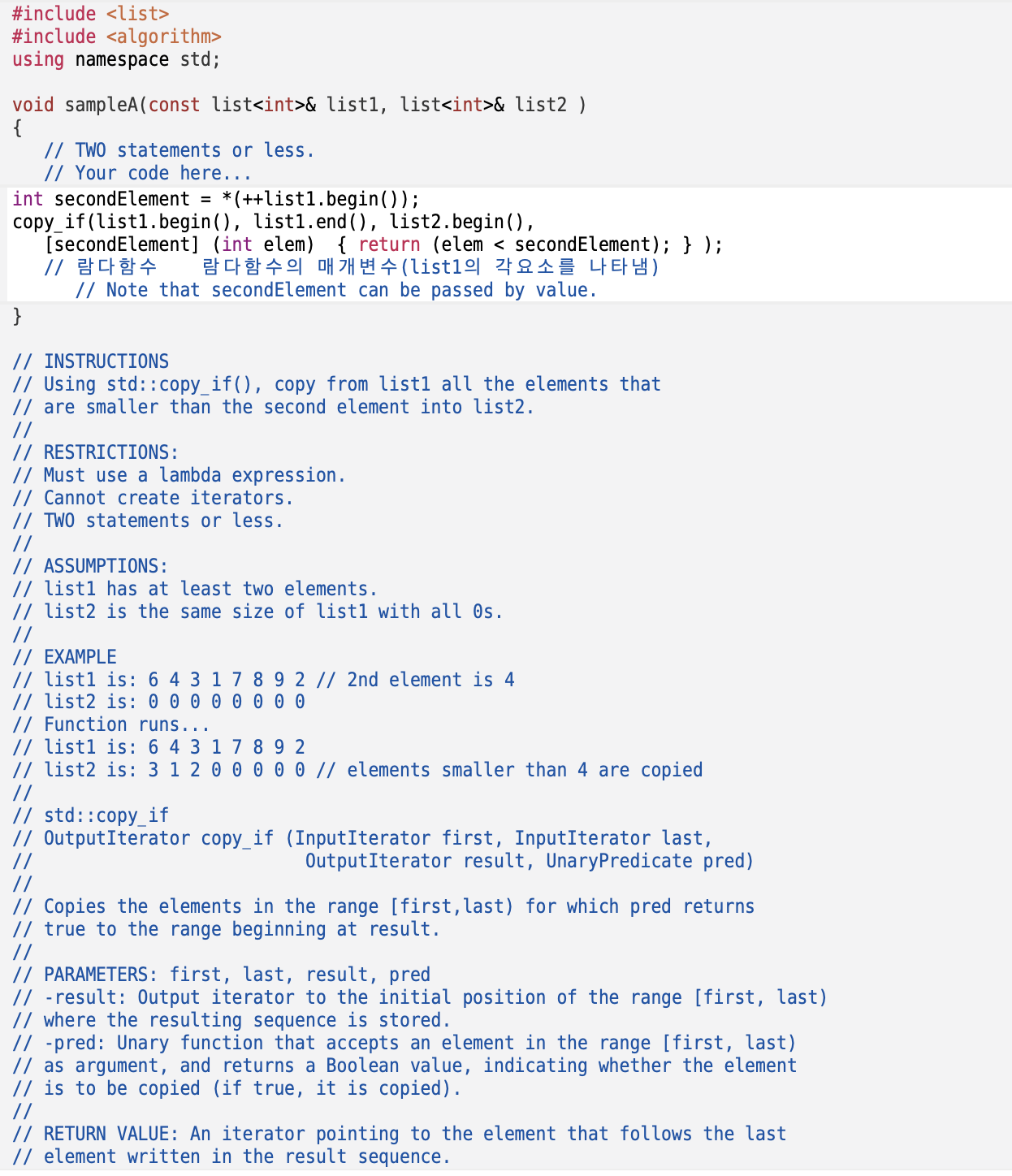
std::fill_n
OutputIterator fill_n (OutputIterator first, Size n, const T& val);
Fill sequence with value
Assigns val to the first n elements of the sequence pointed by first.
Parameters
- first: Output iterators to the initial position in a sequence of at least n elements that support being assigned a value of type T.
- n: Number of elements to fill.
- val: Value to be used to fill the range.
Return value
An iterator pointing to the element that follows the last element filled.
- STL algorithms
- About these functions:
- adjacent_find
- Some do not work with all containers. How can you find out which ones do work? By reading their description in cplusplus.com OR by trying them.
- Some require a predicate function. Make sure you try them both ways by writing a non-member function and by using a lambda expression.
- all_of, any_of
- copy, copy_backward, copy_if, copy_n
- count, count_if
- fill, fill_n
- find, find_if
- for_each
- is_sorted
- remove, remove_if
- replace, replace_if
- reverse
- rotate
- sort(first, last), sort(first, last, comp)
- swap
- unique
- adjacent_find
The questions will cover:
Linked lists (one or two questions only).
The STL (see the “STL Functions to know” section for more details).
'૮₍˶ᵔ ᵕ ᵔ˶₎ა♡ > coding' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [C++] Queues(10)!! 연습하기 ^ㅅ^ (0) | 2024.04.04 |
|---|---|
| [C++] Stacks(9)!! 연습하기 ^ㅅ^ (0) | 2024.04.04 |
| [C++] STL Algorithms(8)!! 연습하기 ^ㅅ^ (0) | 2024.04.04 |
| [C++] Associative Containers(7)!! 연습하기 ^ㅅ^ (0) | 2024.04.04 |
| [C++] Sequence Containers(6)!! 연습하기 ^ㅅ^ (0) | 2024.04.02 |